Share & grow the world's knowledge!
We want to connect the people who have knowledge to the people who need it, to bring together people with different perspectives so they can understand each other better, and to empower everyone to share their knowledge.

What are the differences between HTML and XHTML?
HTML is the standard markup language for creating web pages. XHTML is a stricter and more well-defined version of HTML. It's frequently used for formatting more complex documents within a stated taxonomy. HTML code: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1 style="background-color: red;Read more
HTML is the standard markup language for creating web pages. XHTML is a stricter and more well-defined version of HTML. It’s frequently used for formatting more complex documents within a stated taxonomy.
HTML code:
XHTML code:
See lessWhat is AJAX?
AJAX is a web development technique for creating asynchronous web applications. AJAX allows you to create dynamic, responsive web applications that can be updated without reloading the page.
AJAX is a web development technique for creating asynchronous web applications. AJAX allows you to create dynamic, responsive web applications that can be updated without reloading the page.
See lessWhat is a CDN?
A content delivery network (CDN) is a system for delivering content to users based on geographic location. CDNs can deliver websites, software applications, and other types of digital content.
A content delivery network (CDN) is a system for delivering content to users based on geographic location. CDNs can deliver websites, software applications, and other types of digital content.
See lessWhat are the supported standard data types in Python?
The supported standard data types in Python include: Lists Numbers Strings Dictionaries Tuples
The supported standard data types in Python include:
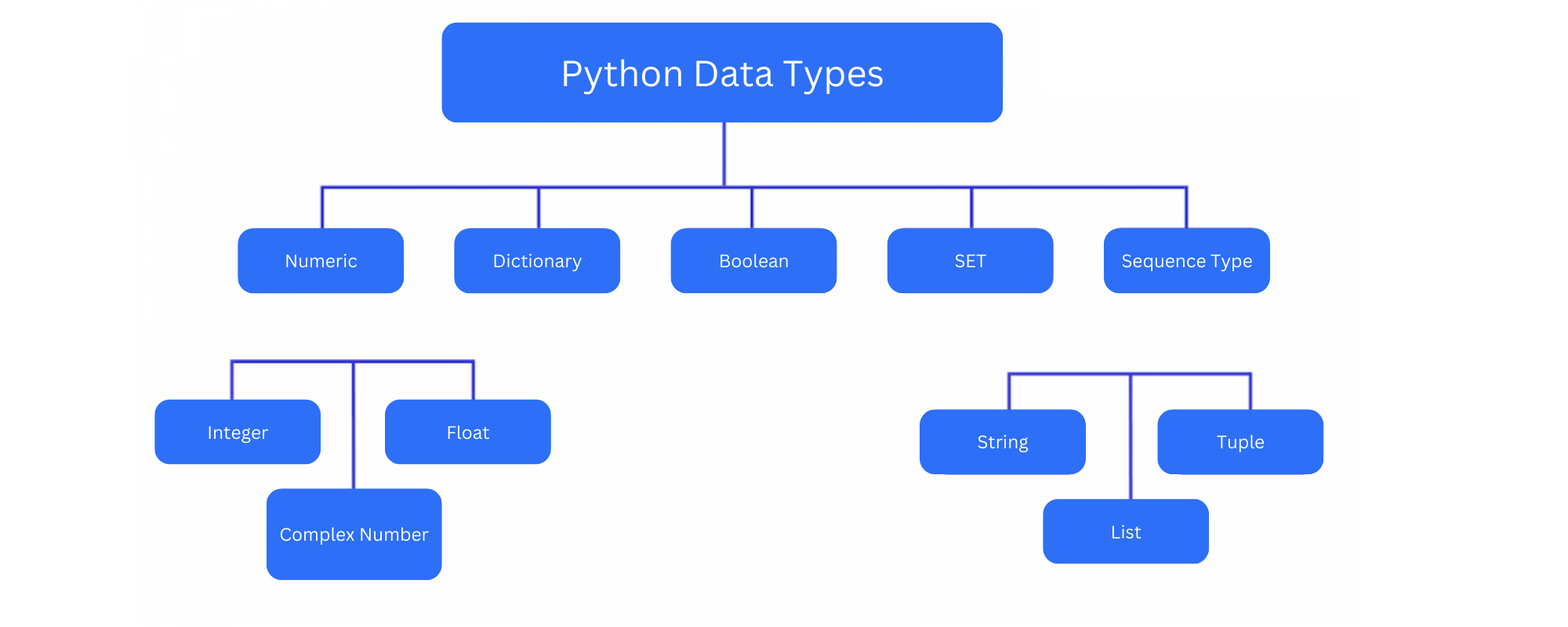
See lessBriefly explain some characteristics of Python.
Python is a general purpose, high-level, interpreted language. It was specifically developed with the purpose of making the content readable. Python has often been compared to the English language, and it also has fewer syntactic constructions compared to other languages.
Python is a general purpose, high-level, interpreted language. It was specifically developed with the purpose of making the content readable. Python has often been compared to the English language, and it also has fewer syntactic constructions compared to other languages.
See lessWhat are some distinct features of Python?
Some distinct features of Python are: Structured and functional programming is supported. It can be compiled to byte code to create larger applications. Supports high-level dynamic data types. Supports checking of dynamic data types. Applies automated garbage collection. It could be used effectivelyRead more
Some distinct features of Python are:
- Structured and functional programming is supported.
- It can be compiled to byte code to create larger applications.
- Supports high-level dynamic data types.
- Supports checking of dynamic data types.
- Applies automated garbage collection.
- It could be used effectively along with Java, COBRA, C, C++, ActiveX, and COM.
See lessWhy do we use the Pythonstartup environment variable?
The variable consists of the path in which the initialization file carrying the Python source code can be executed. This is needed to start the interpreter.
The variable consists of the path in which the initialization file carrying the Python source code can be executed. This is needed to start the interpreter.
See lessWhat is the Pythoncaseok environment variable?
The Pythoncaseok environment variable is applied in Windows with the purpose of directing Python to find the first case insensitive match in an import statement.
The Pythoncaseok environment variable is applied in Windows with the purpose of directing Python to find the first case insensitive match in an import statement.
See lessWhat are tuples?
Tuples are a sequence data type with immutable values in Python. The number of values i tuples is separated by commas.
Tuples are a sequence data type with immutable values in Python. The number of values i tuples is separated by commas.
See lessWhat is the major difference between tuples and lists in Python?
There are several major differences between tuples and lists in Python, which include the following: Tuples List Tuples are similar to a list, but they are enclosed within parentheses, unlike the list The list is used to create a sequence The element and size can be changed The element and size cannRead more
There are several major differences between tuples and lists in Python, which include the following:
What are positive and negative indices?
Positive indices are applied when the search begins from left to right. In negative indices, the search begins from right to left. For example, in the array list of size n the positive index, the first index is 0, then comes 1, and until the last index is n-1. However, in the negative index, the firRead more
Positive indices are applied when the search begins from left to right. In negative indices, the search begins from right to left. For example, in the array list of size n the positive index, the first index is 0, then comes 1, and until the last index is n-1. However, in the negative index, the first index is -n, then -(n-1) until the last index -1.
See lessWhat is the permitted length of the identifier?
The length of the identifier in Python can be of any length. The longest identifier will be from PEP – 8 and PEP – 20.
The length of the identifier in Python can be of any length. The longest identifier will be from PEP – 8 and PEP – 20.
See lessWhat is namespace in Python?
A namespace is a naming system used to make sure names are unique to avoid naming conflicts
A namespace is a naming system used to make sure names are unique to avoid naming conflicts
See lessIs indentation necessary in Python?
Indentation is required in Python if not done properly the code is not executed properly and might throw errors. Indentation is usually done using four space characters.
Indentation is required in Python if not done properly the code is not executed properly and might throw errors. Indentation is usually done using four space characters.
See lessDefine a function in Python.
A block of code that is executed when it is called is defined as a function. The keyword def is used to define a Python function.
A block of code that is executed when it is called is defined as a function. The keyword def is used to define a Python function.
See lessWhat are the limitations of Python?
There are limitations to Python, which include the following: It has design restrictions. It is slower when compared with C and C++ or Java. It is inefficient for mobile computing. It consists of an underdeveloped database access layer.
There are limitations to Python, which include the following:
- It has design restrictions.
- It is slower when compared with C and C++ or Java.
- It is inefficient for mobile computing.
- It consists of an underdeveloped database access layer.
See lessDo runtime errors exist in Python? Give an example
Yes, runtime errors exist in Python. For example, if you are duck typing and things look like a duck, then it is considered a duck even if that is just a flag or stamp. The code, in this case, would be a run-time error. For example, Print “askthescience.com” would result in the runtime error of theRead more
Yes, runtime errors exist in Python. For example, if you are duck typing and things look like a duck, then it is considered a duck even if that is just a flag or stamp. The code, in this case, would be a run-time error. For example, Print “askthescience.com” would result in the runtime error of the missing parenthesis that is required by print ( ).
See lessCan we reverse a list in Python?
Yes, we can reserve a list in Python using the reverse() method. The code is as follows: defreverse(s): str = "" for i in s: str = i + str return str
Yes, we can reserve a list in Python using the reverse() method. The code is as follows:
See lessdefreverse(s):str = ""
for i in s:
str = i + str
return str
Can we use a break and continue together in Python? How?
Break and continue can be used together in Python. The break will stop the current loop from execution, while the jump will take it to another loop.
Break and continue can be used together in Python. The break will stop the current loop from execution, while the jump will take it to another loop.
See lessIn how many ways can we apply reverse strings?
There are five ways in which the reverse string can be applied: Loops Recursions Stacks Extended slice syntax Reversed function
There are five ways in which the reverse string can be applied:
- Loops
- Recursions
- Stacks
- Extended slice syntax
- Reversed function
See lessDefine slicing in Python.
Slicing refers to the mechanism to select the range of items from sequence types like lists, tuples, strings.
Slicing refers to the mechanism to select the range of items from sequence types like lists, tuples, strings.
See lessWhat are the different stages of the life cycle of a thread?
The different stages of the life cycle of a thread are: Stage 1: Creating a class where we can override the run method of the Thread class. Stage 2: We make a call to start() on the new thread. The thread is taken forward for scheduling purposes. Stage 3: Execution takes place wherein the thread staRead more
The different stages of the life cycle of a thread are:
- Stage 1: Creating a class where we can override the run method of the Thread class.
- Stage 2: We make a call to start() on the new thread. The thread is taken forward for scheduling purposes.
- Stage 3: Execution takes place wherein the thread starts execution, and it reaches the running state.
- Stage 4: Thread waits until the calls to methods including join() and sleep() take place.
- Stage 5: After the waiting or execution of the thread, the waiting thread is sent for scheduling.
- Stage 6: Running thread is done by executing the terminates and reaching the dead state.
See lessWhat are relational operators, assignment operators, and membership operators?
The purpose of relational operators is to compare values. The assignment operators in Python can help in combining all the arithmetic operators with the assignment symbol. Membership operators in Python with the purpose to validate the membership of a value in a sequence.
- The purpose of relational operators is to compare values.
- The assignment operators in Python can help in combining all the arithmetic operators with the assignment symbol.
- Membership operators in Python with the purpose to validate the membership of a value in a sequence.
See lessHow are identity operators different from membership operators?
Unlike membership operators, the identity operators compare the values to find out if they have the same value or not.
Unlike membership operators, the identity operators compare the values to find out if they have the same value or not.
See lessWhat are Python decorators?
A specific change made in Python syntax to alter the functions easily are termed as Python decorators.
A specific change made in Python syntax to alter the functions easily are termed as Python decorators.
See lessDifferentiate between list and tuple.
Tuple is not mutable it can be hashed eg. key for dictionaries. On the other hand, lists are mutable.
Tuple is not mutable it can be hashed eg. key for dictionaries. On the other hand, lists are mutable.
See lessDraw a comparison between the range and xrange in Python.
In terms of functionality, both range and xrange are identical. Both allow for generating a list of integers. The main difference between the two is that while range returns a Python list object, xrange returns an xrange object. Xrange is not able to generate a static list at runtime the way range dRead more
In terms of functionality, both range and xrange are identical. Both allow for generating a list of integers. The main difference between the two is that while range returns a Python list object, xrange returns an xrange object.
Xrange is not able to generate a static list at runtime the way range does. On the contrary, it creates values along with the requirements via a special technique called yielding. It is used with a type of object known as generators.
If you have an enormous range for which you need to generate a list, then xrange is the function to opt for. This is especially relevant for scenarios dealing with a memory-sensitive system, such as a smartphone.
The range is a memory hog. Using it requires much more memory, especially if the requirement is gigantic. Hence, in creating an array of integers to suit the needs, it can result in a memory error and ultimately lead to a crash.
See lessWhat is a binary search? When is it best used?
A binary search is an algorithm that starts with searching from the middle element. If the middle element is not the target element then it checks if it should search the lower half or the higher half. The process continues until the target element is found. The binary search works best when appliedRead more
A binary search is an algorithm that starts with searching from the middle element. If the middle element is not the target element then it checks if it should search the lower half or the higher half. The process continues until the target element is found.
The binary search works best when applied to a list with sorted or ordered elements.
See lessWhat is a queue? How is it different from a stack?
A queue is a form of linear structure that follows the FIFO (First In First Out) approach for accessing elements. Dequeue, enqueue, front, and rear are basic operations on a queue. Like a stack, a queue can be implemented using arrays and linked lists. In a stack, the item that is most recently addeRead more
A queue is a form of linear structure that follows the FIFO (First In First Out) approach for accessing elements. Dequeue, enqueue, front, and rear are basic operations on a queue. Like a stack, a queue can be implemented using arrays and linked lists.
In a stack, the item that is most recently added is removed first. Contrary to this, in the case of a queue, the item least recently added is removed first.
See lessWhat is a stack? State some applications.
A stack is a linear data structure that follows either the LIFO (Last In First Out) or FILO (First In Last Out) approach for accessing elements. Push, pop, and peek are the basic operations of a stack. Some applications of a stack are: Checking for balanced parentheses in an expression The evaluatioRead more
A stack is a linear data structure that follows either the LIFO (Last In First Out) or FILO (First In Last Out) approach for accessing elements. Push, pop, and peek are the basic operations of a stack.
Some applications of a stack are:
- Checking for balanced parentheses in an expression
- The evaluation of a postfix expression
- Implementing two stacks in an array
- Infix to postfix conversion
- Reversing a string
See less